| 1. | Create types using object-orientated principles. Categorise your data models into types (objects). This will greatly improve readability of your implementation, ease maintenance, and reduce coding. |
| 2. | Use constants to save frequently used fixed values. For example, a warning message with fixed content that is used in several scenarios. Not only is typing the warning message in every scenario tedious, but if the message changes, multiple updates are required. Instead, create a constant instance, such as WARNING MESSAGE. Use this instance whenever you need to use the value. If the message changes, you only need to update the instance to apply the change globally. |
The naming convention for constants is all CAPS.
It is recommended that you group constants in a folder and create an instance of type CONSTANTS. This may be saved in a common project for reuse across projects.
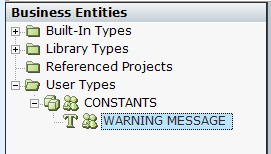
| 3. | Organise your business entities. |
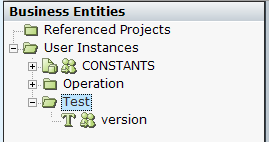
CONSTANTS: Where you create all constants.
Operation: Where you create all your operational business entities.
Test: Where you put business entities that are used for testing purposes.
